Search
How will AI Benefit Africa?
Business and advices
According to IFC’s Mary-Jean Moyo, AI could help combat poverty, joblessness and a host of other challenges in Africa.
To illustrate this, she offered a number of examples such as the use of AI in western Cameroon by the Local Farmers to diagnose and suggest a course of treatment for plants stricken by diseases.
Developed by Agrix Tech, the app allows Local farmers to take a photo of the defective plant and the AI-based smartphone app in 10 seconds only, suggests a treatment, reading it aloud in their Local Language.
This technology, if scaled up, could be used to improve farm yields by helping farmers identify defective crops rapidly, and provide treatment.
If managed appropriately, artificial intelligence could benefit and revolutionize a variety of other industries in Africa—from farming to banking and transportation, according to a new report from IFC, a member of the World Bank Group.
The Government’s role to Play

However, to make this happen, African governments need to play a big part by supporting and engaging with businesses and investors who are already developing AI products and services that could benefit their countries and Africa as a whole.
Unfortunately, the news isn't that good: According to Oxford's Insights in its ‘Government AI Readiness Index 2022,’ (which shows how governments across the continent are turning to AI to improve their services and gain strategic economic advantages), the average score of the 46 Sub-Saharan African countries included in the index was 29.38 —the lowest globally.
The Sub-Saharan region was ranked bottom of the spectrum, with 21 out of the 25 lowest scores belonging to Sub-Saharan African countries. The region scores particularly low in the Technology Sector pillar, with an average score of 20.96.
With a score of 53.38 / 100, Mauritius leads the Continent as a whole and ranks 57th globally. Mauritius scored especially high in the Governance pillar and is the only country in the region to have published a national AI strategy to Improve their Country.
Mauritius with a score of 53.38 out of 100 is the most AI-ready African public sector, followed by Egypt (49.32), and South Africa (47.74) with no African Country featuring in the top 50 Worldwide.

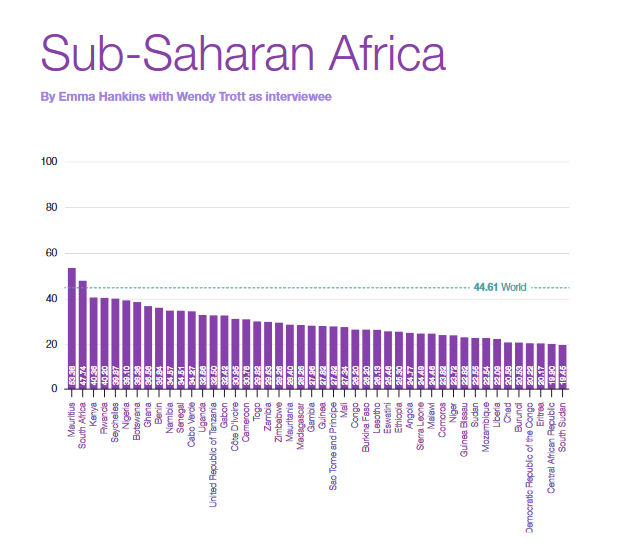
As the relatively low scores across the region suggest, there are many barriers to progress on AI readiness in Sub-Saharan Africa. While broad-band coverage has increased in recent years, the majority of people in the region still lack access to mobile internet, due in part to high device and data costs.
According to regional expert Wendy Trott, Senior Associate at ALT Advisory, the above mentioned barriers to progress need to be solved by the government in order to ensure that the benefits of AI can be fully realized in Sub-Saharan Africa and Africa as a whole.
How Various African Industries are Benefiting from A.I despite the challenges

Focus: The Healthcare Industry, Agriculture & Agro-processing sector, Banking & Finance Sector, and the Marketing Industry
According to research, the introduction of artificial intelligence into economies in Africa, Oceania and other Asian markets could boost GDP by 5.6 percent—or about $11 trillion (excluding China and developed Asia). This shows that economically, Africa will benefit significantly from AI.
But as mentioned above, Africa needs to improve and solve a lot of their current problems to ease the way for AI going forward because as a matter of fact, AI wouldn’t solve all of Africa’s problems.
Despite the challenges that African industries face in adopting artificial intelligence, many industries are already reaping some of its benefits.
1. The Healthcare Industry
Case Study: Rwanda’s Viebeg Technologies
According to a report published on September 9, 2020—"Reimagining Global Health through Artificial Intelligence: The Roadmap for AI Maturity"—low-income countries may soon outperform high-income states in the adoption of artificial intelligence (AI) based health technologies.
The report also notes that African countries have the potential to be the fastest adopters of AI-based health technologies due to a lack of existing systems—but warns that these nations stand to lose out the most if governments don't seize this opportunity and invest more in artificial intelligence.
One of the break-through startups currently applying AI in the medical sector is Rwanda’s Viebeg Technologies, which uses Artificial Intelligence to manage supply chain processes (from shipping and warehousing, distribution of supplies and inventory management), ensuring the availability of precise medical supplies for healthcare facilities.
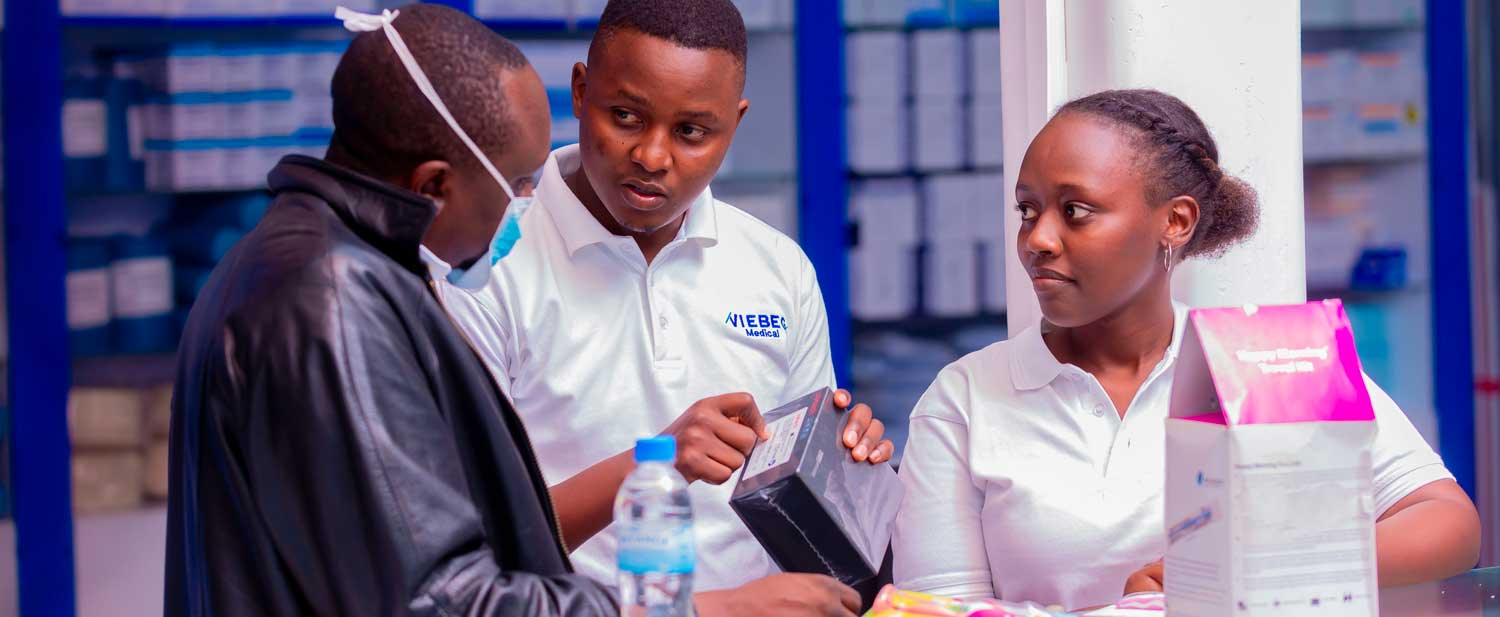

Viebeg Technologies Co-founder Tobias Reiter says that the firm's AI-driven medical procurement platform directly connects healthcare providers with manufacturers. This removes brokers and middlemen from the value chain, generating cost savings of up to 40 percent for customers.
Before Viebeg Technologies, medical facilities in Rwanda didn’t have the right medical supplies and reports showed that every five minutes, people died from conditions that could have been prevented if african medical facilities had the right medical supplies.
This goes to show how important AI is for healthcare. The World Health Organization estimates that more than half of the world’s population lives in areas with a shortage of health workers, and the demand for medical supplies will grow by 4 percent every year. Thus, the need for more innovations such as Viebeg Technologies.
Others:
Other companies such as Zipline, an AI technology that powers drones that are used to deliver medical supplies to Isolated communities. Zipline developed a system where drones are catapulted by zip wire into the air. The drones then travel at 80mph, releasing their delivery when they reach their destination.
For more about Zipline, check out this Article.
2. Agriculture and Agro-processing Sector
Case Study: Cameroon’s Agrix Tech
Agriculture is crucial to the economic well-being of Africa. Over 60% of sub-Saharan Africans are smallholder farmers, and nearly a quarter of the Continent's GDP comes from agriculture.
Although agriculture serves an important role in the region, there is a lot of room for improvement. Modernizing farming practices would help African families increase their incomes and build stronger, more resilient farms. Artificial Intelligence (AI) could play an important role in this increased production goal.
The most well-known use of AI technology in agriculture is precision agriculture. This AI technology is used to detect pests and disease and nutrition in plants.
The system identifies and targets weeds and diseases, then determines the appropriate herbicide type (and amount) or treatment needed to kill those weeds and diseases. This highly efficient process prevents overuse of chemicals so less toxins find their way into food humans ultimately consume.
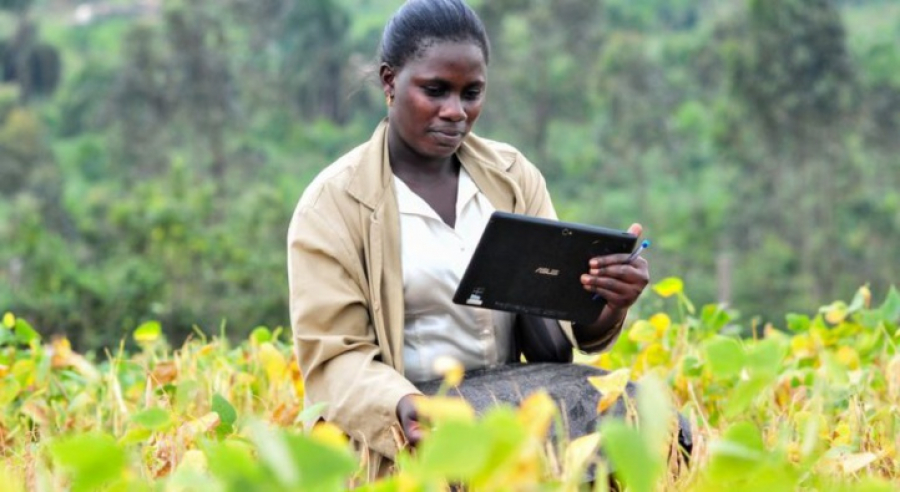

Many methods of AI have already been implemented in Africa. For example, in Cameroon, the Agrix Tech app helps local farmers scan their unhealthy plants, with the recorded video automatically analyzed using machine learning techniques and the farmer is then provided with sustainable and environmentally-friendly treatment recommendations.
The app also helps farmers during the whole production cycle – seeding, growing and storage – through advice and task reminders.
AI has the potential to make African farmers more resilient to the inevitable agricultural threats of the climate crisis. It also has potential to generally increase crop yields and help local farmers use materials more efficiently and sustainably.
3. Banking and Finance Sector
Case Study: Nigeria’s Zenith Bank AI-backed chatbot called ZiVA
With the growing implementation of AI in banking, a new range of services has been made available to better meet customers' changing needs. Chatbots are a relatively new phenomenon in banking, with the capabilities of these tools rapidly advancing as a result of technological advancements.
According to Oracle, a chatbot is a computer program that simulates and processes human conversation (either written or spoken), allowing humans to interact with digital devices as if they were communicating with a real person.
In recent years, many African Banks have launched Chatbots, one of which is Nigeria’s Zenith Bank.

Nigerian financial organization Zenith Bank introduced their AI-backed chatbot called ZiVA (Zenith Intelligent Virtual Assistant) on WhatsApp which enables the bank’s customers to perform financial transactions and enjoy real-time customer service from their mobile phones on a 24-hour basis.
With this new service, customers can open new accounts, receive instant notifications of transactions and check their balances on-the-go. They can also transfer funds or top up airtime if needed.
In addition, they can confirm checks, fill out forms to pay bills and apply for loans. They can also request mini statements of their accounts or blocks on said account if there is any suspicious transaction.
This solution has allowed Zenith bank to reduce its communication costs, as many customers used the Unstructured Supplementary Service Data (USSD) platform to engage with the organization.
Also, it has helped the bank streamline its operations, as customers can now access their accounts anytime and anywhere. This has reduced staff workload and improved customer satisfaction levels.
4. The role of AI in Marketing: How AI can benefit Brands in Africa
Case Study: South Africa’s Christopher Africa
Online advertising has become an integral part of many businesses in Africa, including Cameroon and with the rise of social media platforms, like Facebook and Instagram, businesses have realized the potential of advertising to reach a wider audience and connect with their audience on a personal level through personalized ads and messages.
A recent study from Mckinsey & Company showed that consumers are more likely to purchase from Brands that personalize.
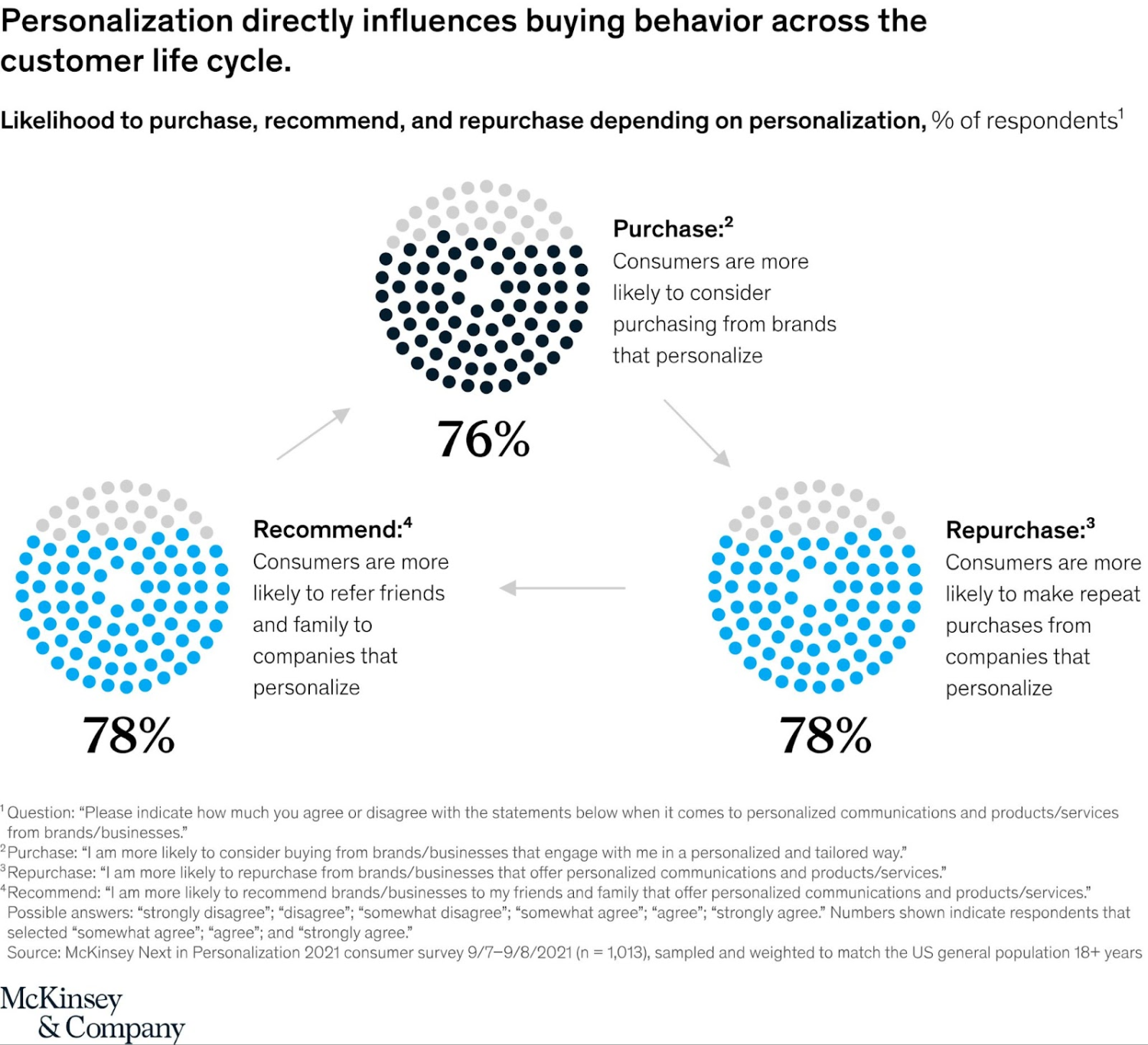
The study revealed that over three-quarters (76%) of consumers said that receiving personalized communications was a key factor in prompting their consideration of a brand, and 78 percent said such content made them more likely to repurchase from brands after receiving such messages.
Personalization creates a cycle of loyalty: brands that personalize their interactions with customers can retain them for longer periods and earn more revenue in the long run.
Christopher Africa, an artificial intelligence software that serves real-time brand responses to relevant conversations on social media, and delivers mass personalisation at scale to drive qualified engagements and impressions, clearly understood the importance of Personalization.
This technology exists to provide marketers with the ability to advertise to consumers when it is relevant by tapping into relevant social media conversations in real-time.
How Christopher works

The software is regarded as ‘ground-breaking’ by marketing professionals across the world with over 100 world-class brands already using the service.
The emergence of Christopher in the media and advertising space will enable brands in Africa to improve real-time customer targeting on social media with relevant brand messages, reduce advertising cost, minimize digital media waste and boost sales.
Final Thoughts
AI can help grow the economies of Africa and improve people's lives. It has the potential to increase productivity, make healthcare more accessible, facilitate marketing efforts by local businesses, and enhance crop yields.
Without taking advantage of the opportunities AI presents, Africa will continue to lag behind countries in the global world.
Stakeholders in Africa, especially the government, need to establish strong governance structures and infrastructures to improve on the adoption and use of AI technologies which will have a massive influence on Africa's economy.
Thanks for reading this Article proposed by ALM Creative Studios. We will love to hear your thoughts on this.
Stay tuned for more blog posts like this and our upcoming publications where we aim to further explore the impact and scalability of AI applications in Africa.




